Why WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE and READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE Are Security Risks in Android Apps ??
In the Android ecosystem, requesting the READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE and WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permissions may seem harmless—after all, many apps need to access photos, documents, or videos. However, enabling these permissions opens the door to serious security and privacy vulnerabilities.
What’s the Risk?
These permissions grant your app access to the shared external storage on the device. This includes files created by other apps—and vice versa.
Key Vulnerabilities:- Data Leakage: With READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE, your app can access sensitive files that users may not expect it to read—like documents, images, or logs from other apps.
- Data Tampering or Deletion: WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE lets your app modify or delete files anywhere in external storage, including other apps' data or system-related content.
- Malicious File Injection: A malicious app can place files in shared storage that your app might unknowingly read or execute—leading to attacks like path traversal or remote code execution.
- Privacy Compliance Violations: Overly broad access can breach privacy laws such as GDPR or CCPA, especially if personal data is accessed without explicit user consent.

How to Disable READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE and WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE Permissions
Step 1:
Open AndroidManifest.xml Locate the AndroidManifest.xml file in your project’s app/src/main/ directory.Step 2:
Remove These Permission Lines (if present)<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
If your app needs to read/write files, replace shared external storage access with one of the following:
For app-specific files:

For images/videos using MediaStore (Android 10+):
Use the MediaStore API to safely access media without needing broad permissions.For accessing documents or user files, use an Intent like:
This does not require storage permissions, as it’s a user-granted file access.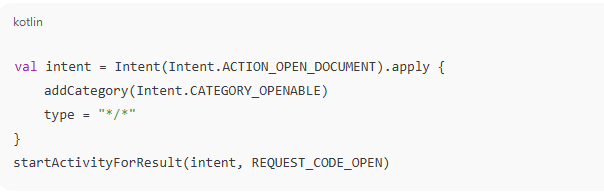
Set Target SDK to 30 or Higher (Optional but Recommended)
In your build.gradle (app-level), update: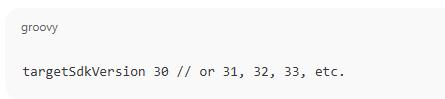 This enables Scoped Storage enforcement, even if legacy code exists.
This enables Scoped Storage enforcement, even if legacy code exists.

