SQL Injection Leading to Authentication Bypass: A Hidden Entry Point
What is the Vulnerability?
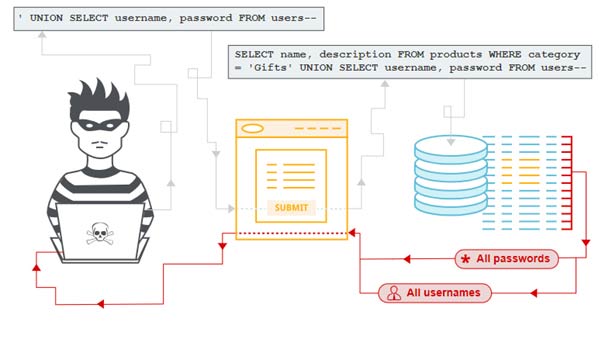
A form of web application vulnerability known as SQL Injection happens when user input is not adequately cleaned up before being incorporated into SQL queries. Without adequate validation or parameterisation, a weak login mechanism in the context of authentication simply enters user-provided values (such as the username and password) into a SQL query. Example of vulnerable SQL query:

An attacker can insert malicious SQL code to change the query's intended logic if the application is unable to handle special characters correctly. For example, by typing:
- Username: 'OR '1'='1
- The password is --

In this case, '1'='1' is always true, and the remainder of the query is commented out. By doing this, authentication is essentially circumvented, allowing the attacker to log in without legitimate credentials.
Impact of the Vulnerability?
There are serious repercussions when SQL Injection occurs at the authentication endpoint:
- Unauthorised Access: Attackers can log in as administrators or any other user.
- Privilege Escalation: Attackers may be able to take administrative control of the application if they continue to exploit it.
- Data Breach: After logging in, attackers may be able to access private user information or run additional queries.
- Total System Compromise: Attackers may occasionally combine SQL Injection with additional flaws to compromise the server or backend database.
- Legal and Reputational Damage:If personal information is made public, organisations may be sued or lose the trust of users.
Solution to fix the Vulnerability:
To protect against SQL Injection and authentication bypass, developers should take the following steps:
- Use Parameterized Queries (Prepared Statements): Avoid dynamic SQL construction. Use placeholders for user input to ensure its treated as data, not code.
- Validate and sanitize input: Make sure usernames, passwords, and other fields match expected formats. Reject any suspicious or unexpected characters.
- Secure password handling: Hash and salt passwords with strong algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2. This way, even if attackers access the database, passwords stay unreadable.
- Restrict database privileges: Assign the application’s database user only the permissions it needs, nothing more.


