Missing HTTP Security Headers
Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS)
Impact if missing:
Users may access the site over insecure HTTP, making them vulnerable to SSL stripping attacks.
Solution: Set this header to enforce HTTPS:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
Content-Security-Policy (CSP)
Impact if missing:
Higher risk of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), data injection, or clickjacking.
Solution: Define allowed content sources:
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' https://trusted.com Adjust script-src, img-src, etc., to fit your site’s requirements.
X-Frame-Options
Impact if missing:
Site can be embedded in iframes, allowing clickjacking attacks.
Solution:
Disallow framing or allow only your domain: SAMEORIGIN X-Frame-Options: DENY

X-Content-Type-Options
Impact if missing:
Browser may mime-sniff content and interpret it incorrectly, enabling content-type confusion attacks.
Solution:
Prevent content type sniffing: X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Here’s how to add missing security headers in the listed servers/frameworks:
Nginx
Edit: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or site-specific config (/etc/nginx/sites-available/default)
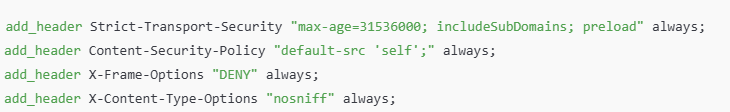 Note: Use always to ensure headers are added even on error pages.
Note: Use always to ensure headers are added even on error pages.
Apache HTTPD
Edit: .htaccess or httpd.conf or virtual host file
 Ensure mod_headers is enabled:
a2enmod headers && systemctl restart apache2
Ensure mod_headers is enabled:
a2enmod headers && systemctl restart apache2
IIS (Windows Server)
Use IIS Manager or web.config:


