Local File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability & Its Fixation
What is the vulnerability?
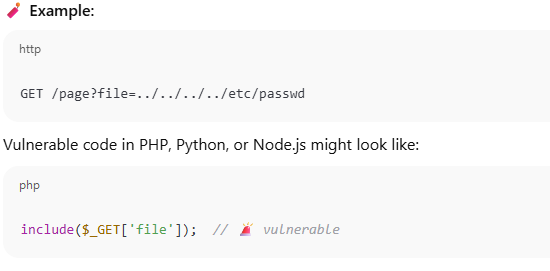
Local File Inclusion (LFI) occurs when a web application dynamically loads or includes files based on user input without proper validation or sanitization.
Attackers exploit LFI to include unintended files from the local filesystem, potentially exposing sensitive data or enabling code execution.

Impact of the Vulnerability
1. Sensitive File Disclosure
- Access OS files like /etc/passwd, config files, credentials
- View environment variables or internal logs
2. Code Execution (when chained)
- Combine with file upload or log injection to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE)
3. Source Code Exposure
- Read source code of backend services (index.php, .env, etc.)
4. Authentication Bypass
- In some cases, attackers can include session files or override logic
Solution to Fix the Vulnerability
- Don’t allow users to define or manipulate file paths directly
- Allow only known-safe files or pages to be included:
- Use realpath() to resolve paths
- Ensure paths are under a controlled directory
- In PHP:
- Disable directory listings
- Set strict file permissions
- Use WAF or mod_security rules to detect traversal attempts (../, %2e%2e)
1. Never Trust User Input for File Paths
2. Use Whitelists

3. Sanitize and Normalize Paths
If dynamic inclusion is required:

4. Disable Remote Inclusion

5. Harden the Server
LFI is simple to exploit and can lead to severe breaches, especially when chained with other vulnerabilities like file upload or RCE. Validate file paths, restrict dynamic includes, and monitor file access closely. Don’t let your app become a file browser for attackers.

