Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) via File Upload
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) via File Upload is a type of attack where an authenticated user is tricked into uploading a file (often malicious or unintended) to a target application, without their consent, by submitting a file upload form from another domain.
This is possible only if the file upload endpoint is vulnerable to CSRF — i.e., it does not implement proper CSRF protection mechanisms such as tokens or same-site cookie policies.
 via File Upload - image.png)
How It Works
1. The victim is authenticated to a target application (e.g., company portal).
2. The attacker hosts a page (e.g., on evil.com) with a hidden HTML form targeting the file upload endpoint.
3. The attacker auto-submits or tricks the victim into submitting a request using the victim’s browser (via a POST form) to upload the malicious file or payload.
4. If the upload endpoint lacks CSRF protection, the file is uploaded using the victim’s session cookie.
How to Prevent CSRF via File Upload
-
Use CSRF Tokens:
- Implement per-request CSRF tokens in all file upload POST forms.
- Server should verify this token before processing any uploaded file.
-
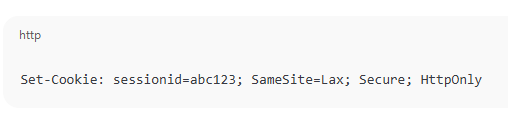
SameSite Cookies:
- Set session cookies with
SameSite=LaxorSameSite=Strict.
- Set session cookies with
-
Validate Content-Type:
- Ensure the Content-Type of the incoming request is valid (
multipart/form-datafor uploads). - Block unexpected
application/x-www-form-urlencodedortext/plainuploads.
- Ensure the Content-Type of the incoming request is valid (
-
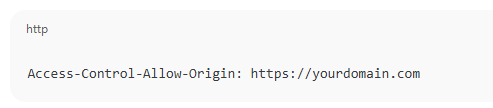
CORS Headers:
- Reject cross-origin requests unless explicitly required.